Splenic cysts
Introduction
Splenic cysts are uncommon findings in clinical practice, with an estimated prevalence of 0.2-0.7% in the general population. Ultrasound serves as the first-line imaging modality for evaluating these lesions due to its non-invasive nature, wide availability, and excellent ability to characterize cystic structures.
Classification of Splenic Cysts
Patients with splenomegaly can present with a variety of symptoms and signs, depending on the underlying cause. The clinical presentation can range from asymptomatic (discovered incidentally) to symptomatic with complications such as Hypersplenism or splenic infarction
Splenic cysts can be broadly classified into two categories:
1. True (Primary) Cysts
These are lined by epithelium and include:
- Congenital (epidermoid) cysts - most common true cysts
- Mesothelial cysts
- Endothelial cysts
2. Pseudal (Secondary) Cysts
These lack an epithelial lining and include:
- Post-traumatic cysts (most common overall)
- Degenerative cysts
- Infectious cysts (e.g., hydatid disease)
Ultrasound features
The sonographic appearance of splenic cysts varies depending on their etiology and content:
Key Ultrasound Characteristics
- Well-defined, rounded or oval lesions
- Thin, smooth walls (except in complicated cases)
- Anechoic or hypoechoic center
- Posterior acoustic enhancement
- No internal vascularity on Doppler
Simple Cysts
Appear as anechoic structures with sharp margins and posterior acoustic enhancement. The walls are typically thin (<1mm) and regular.
Complex Cysts
May demonstrate internal echoes, septations, wall thickening, or calcifications. These features raise suspicion for:
- Hemorrhage
- Infection
- Parasitic infection (e.g., hydatid disease)
- Neoplastic processes
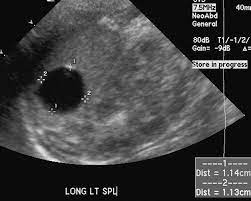
Simple splenic cyst
- Well-defined
- Anechoic
- sharp margins
- Posterior acaustic enhancement
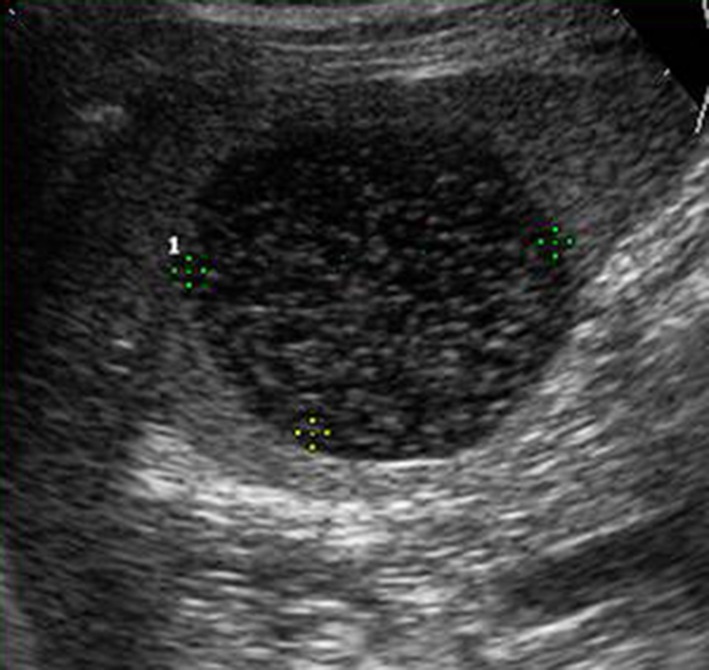
Infected cyst
- Complex cystic lesion with internal echoes
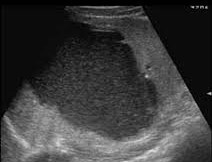
Hemorrhagic cyst
- Well-defined splenic cyst
- Gravity dependent echoes (due to debris or clot formation)
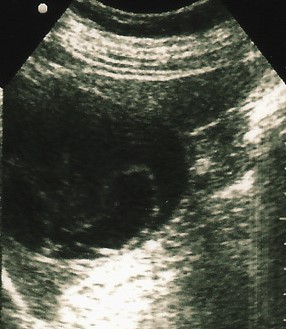
Hydatid cyst
- Well-defined, thin-walled cyst
- Floating membranes within the cyst
Note: Ultrasound is an excellent first-line imaging modality for evaluating splenic cysts. While most splenic cysts are benign and asymptomatic, careful assessment of their sonographic features is essential to identify cases that may require further investigation or treatment. Complex features should prompt consideration of alternative diagnoses and potentially further imaging with CT or MRI.